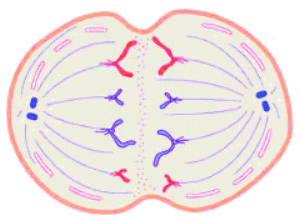
  Mitosis is how a cell replicates its chromosomes and then segregates them, producing two identical nuclei in preparation for cell division. Mitosis is like making a copy of an instruction manual. A cell copies each chromosome, then gives one copy to each of two daughter cells. The copies need to be perfect, or the cells may have trouble following the genetic instructions.
Mitosis is how a cell replicates its chromosomes and then segregates them, producing two identical nuclei in preparation for cell division. Mitosis is like making a copy of an instruction manual. A cell copies each chromosome, then gives one copy to each of two daughter cells. The copies need to be perfect, or the cells may have trouble following the genetic instructions. The process has two main steps: karyokinesis, the division of the cell's nucleus into two identical nuclei, and cytokinesis which is the formation of two distinct daughter cells. Mitosis is responsible for the duplication and division of cells. It ensures the growth and development of multicellular organisms. It also allows the repair of tissues as it replaces damaged or dead cells. Mitosis contributes to the formation and differentiation of various cell types in the growing organism. Chromosomes are thread-like structures located inside the nucleus of cells. Each chromosome is made of protein and a single molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA. Passed from parents to offspring, DNA contains the specific instructions that make each type of living creature unique. The spitting of a nucleus to form two new cells, mitosis is conventionally divided into 6 phases: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis. 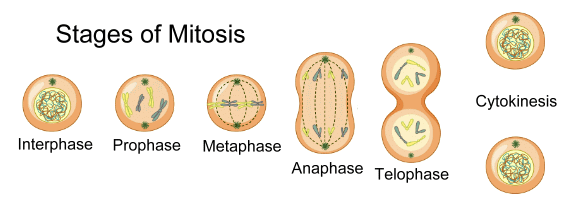 Interphase In interphase, a nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus. The spherical nucleus resembles a ball of wool. The DNA is replicated and join together at the central portion of the chromosome. The chromosome motion is organized to help make division efficient. Prophase In prophase, each replicated chromosome appears as two identical chromatids joined together. The nuclear envelope begins to dissolve. Things begin to move. Metaphase In metaphase, the chromosomes have all lined up in the middle of the cells; smaller chromosomes are directed toward the center while bigger ones are peripheral. Anaphase In anaphase, the daughter chromosomes move toward opposite poles of the cell. By the end of anaphase, the two halves of the cell have an equivalent collection of chromosomes. Telophase In telophase, two daughter nuclei form. The nuclear envelope begins to reappear around each set of chromosomes. Mitosis is now just about complete. Cytokinesis The last step is cytokinesis, which is the physical division of the cell into two separate cells, each with its own nucleus of genetic material, The result is that in an organism, as mitosis happens over and over again, the number of cells begins growing exponentially. 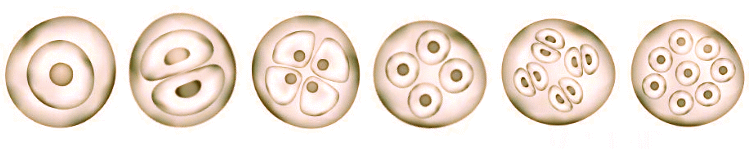 |